Payment Gateways
As a self-hosted ecommerce solution, Commerce handles payments differently from popular software-as-a-service products—instead of providing a fixed list of payment processors, gateways are provided by first-party and community-maintained plugins that build upon a flexible transactions API. This means that stores can support a variety of payment methods, while keeping customer and administrator experience smooth.
To capture live payments, you must install a payment gateway plugin. Commerce comes with two built-in gateways, but they are intended primarily for testing.
In the control panel, navigate to Commerce → Settings → Gateways, and click + New gateway. Each gateway requires different settings—for more detailed instructions, see the plugin’s documentation. Many payment processors require third-party accounts, and provide credentials for communicating with their infrastructure that must be added to the gateway’s configuration.
When providing secrets in the control panel, we recommend using the special environment variable syntax to prevent them leaking into project config.
Payment gateways (and the specific methods they support) generally use one of two payment flows:
- External or offsite gateways: The customer is redirected to a payment portal hosted by the processor, and is returned to your site once a payment is completed. Your site never sees information about the customer’s payment method—instead, the gateway receives and validates a temporary token, and signals to Commerce that the transaction was successful.
- Merchant-hosted or onsite gateways: Payment details are sent directly to your store, and the gateway forwards them to the payment processor. These implementations have much higher risk profiles and are subject to rigorous security requirements under the PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
Most gateways available for Commerce use a tokenization (opens new window) process in the customer’s browser that (at a technical level) has a great deal in common with an offsite gateway, while preserving the smooth checkout experience of an onsite gateway.
#First-Party Gateway Plugins
| Plugin | Gateways | Remarks | 3D Secure Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stripe (opens new window) | Stripe | Uses Stripe’s Payment Intents API; only first-party gateway to support subscriptions | Yes |
| PayPal Checkout (opens new window) | PayPal Checkout | Yes | |
| Sage Pay (opens new window) | SagePay Direct; SagePay Server | Yes | |
| MultiSafepay (opens new window) | MultiSafePay REST | Does not support authorize charges | Yes |
| Worldpay (opens new window) | Worldpay JSON | No | |
| eWay (opens new window) | eWAY Rapid | Supports storing payment information | Yes |
| Mollie (opens new window) | Mollie | Does not support authorize charges | Yes |
| PayPal (opens new window) deprecated | PayPal Pro; PayPal REST; PayPal Express | PayPal REST supports storing payment information | Only PayPal Express |
Additional third-party gateways can be found in the Plugin Store (opens new window).
Before using a plugin-provided gateway, consult the its readme for specifics. Gateways themselves do not implement the logic to process payments against financial institutions, and therefore have external dependencies and fees.
#Built-in Gateways
#Dummy Gateway
The Dummy gateway is only for testing with placeholder credit card numbers. A “valid” card number (passing a simple Luhn (opens new window) check) ending in an even digit will simulate a successful payment. If the last digit is odd, the gateway will treat it as a failed payment:
| Example Card Number | Dummy Gateway Response |
|---|---|
| 4242424242424242 | Success |
| 4444333322221111 | Failure |
Do not use real credit card information when testing, as it may be captured as plain text in logs, caches, or the database.
#Manual Gateway
The Manual payment gateway does not communicate with any third party, nor accept any additional data during checkout.
You should use the Manual payment gateway to accept checks, bank deposits, or other offline payment: it “authorizes” all payments, allowing the order to be submitted into the default order status. Once the payment is received, the payment can be manually marked as “captured” in the control panel by an administrator.
Multiple manual gateways can be created to track different kinds of offline payments, like Cash or Check. Each gateway can also be made available to customers only when their order total is zero—perfect for things like free sample packs or event tickets.
#Adding Gateways
Additional payment gateways can be added to Commerce with relatively little work. All our first-party gateway plugins (with the exception of Stripe) use the Omnipay library (opens new window) and can be used as a point of reference when creating your own.
Gateways can only be configured in development environments with allowAdminChanges enabled. If you need some information about a gateway in a live environment, use the gateways/list or gateways/webhook-url console commands.
See the Extending Commerce section’s Payment Gateway Types page to learn about building your own gateway in a plugin or module.
#Gateway Conditions 5.4.0+
In a gateway’s settings screen, the Match Order condition builder allows you to restrict a gateway to orders that match specific criteria.
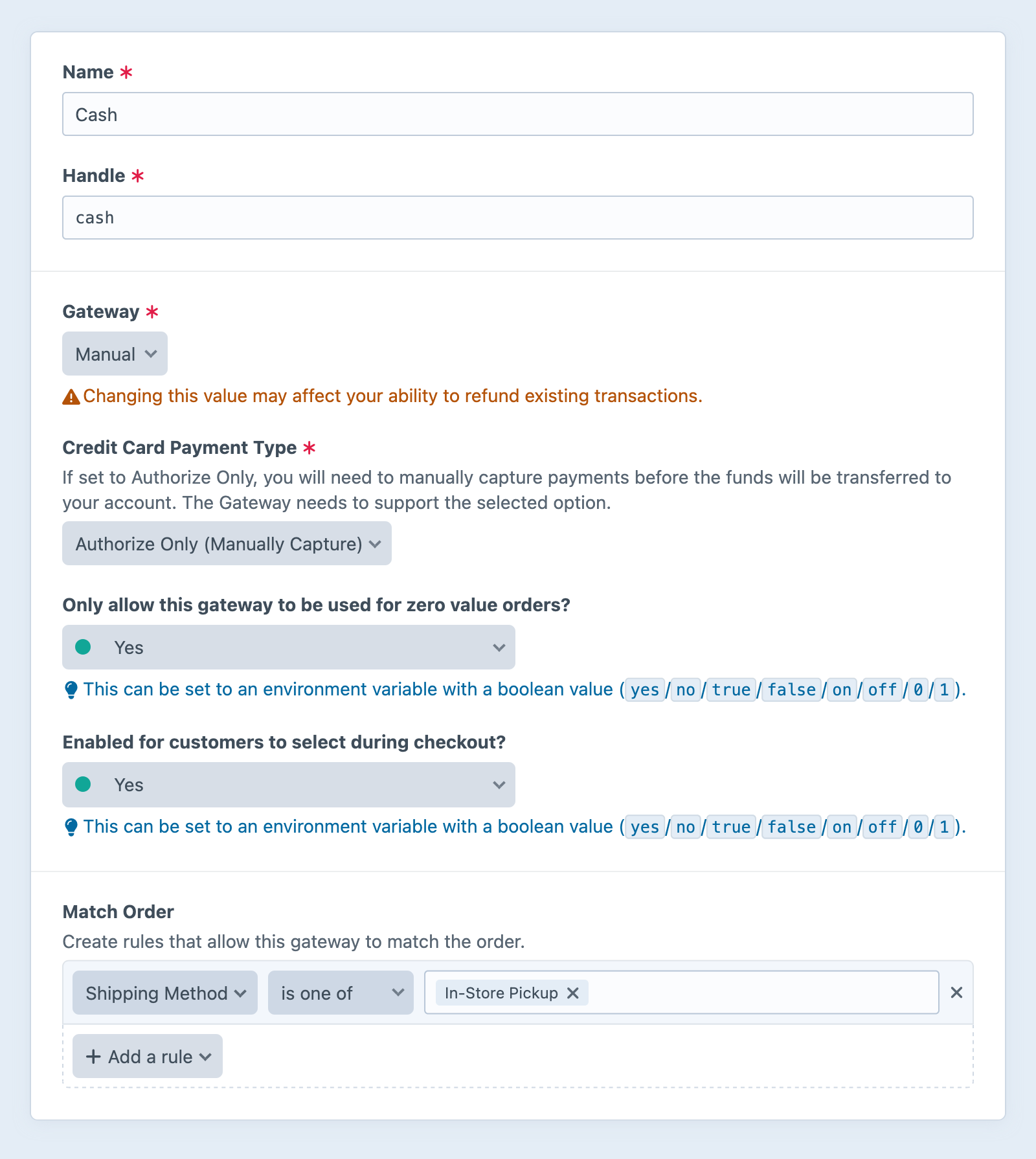
Here, we’ve made the Cash gateway available only on orders that the customer will pick up in-store.
#Storing Config Outside of the Database
When you’re configuring gateways in the Craft control panel, we recommend using environment variables so environment-specific settings and sensitive API keys don’t end up in the database or project config.
Gateways may expose options via their plugin settings file (i.e. config/commerce-stripe.php), but they will apply to all instances of that gateway.
#Payment Sources
Some gateways support storing and reusing payment sources for a more streamlined customer experience. This is typically a limitation of the payment processor’s API—Commerce itself makes the functionality available to all gateway plugins.
The following first-party provided gateways support payment sources:
- Stripe
- PayPal REST (Deprecated)
- eWAY Rapid
#3D Secure Payments
3D Secure is an important authentication step for customers in many markets. If a payment has been completed using 3D Secure authentication, the liability for fraudulent charges is shifted from the merchant to the card issuer. Support for this feature depends on the gateway used and its settings.
Transactions that require additional offsite authorization (indicated by the processor) are typically marked as a “Redirect,” and get completed or captured after the customer is returned to the store. Each gateway handles this in a way that is specific to the payment processor’s
If you see payments stuck in “Redirect” status, it may be because the customer never completed an authorization challenge. Gateways can report completed-but-failed challenges back to Commerce, so that the customer may retry.
Gateways that support 3D Secure (or other asynchronous verification processes, like installment plans) may require webhooks to be configured for payments to work as expected.
#Partial Refunds
All first-party provided gateways support partial refunds. You may only issue refunds to the original payment method used in a transaction, and up to the amount paid in that transaction. If multiple payments were made, you must refund them separately.
#Templating
#craft.commerce.gateways.getAllCustomerEnabledGateways()
Returns all payment gateways available to the customer.
{% set gateways = craft.commerce.gateways.getAllCustomerEnabledGateways() %}
{% if gateways is empty %}
{# This is an awkward state, but possible if all enabled gateways have conditions that are too restrictive! #}
<p>No payment methods available.</p>
{% else %}
<form method="post">
{{ csrfInput() }}
{{ actionInput('commerce/cart/update-cart') }}
{{ redirectInput('checkout/payment') }}
<label for="gatewayId">Payment Method</label>
<select name="gatewayId" id="gatewayId">
{% for id, name in gateways %}
{{ tag('option', {
value: id,
selected: id == cart.gatewayId,
text: name,
}) }}
{% endfor %}
</select>
<button>Save + Continue</button>
</form>
{% endif %}
Once a gateway is selected, you’ll need to display the selected gateway’s payment form using gateway.getPaymentFormHtml({}).