Categories
Craft supports user-managed, hierarchical taxonomies for content via categories.
Categories are one of Craft’s built-in element types, and are represented throughout the application as instances of craft\elements\Category (opens new window).
With the release of Craft 4.4, we began consolidating features of other element types into entries.
As part of that process, we introduced a console command that can automate the conversion of categories to structure sections:
php craft entrify/categories myCategoryGroupHandle
Read more about this transition (opens new window) on our blog.
#Category Groups
Every category belongs to a category group, which defines…
- …a name;
- …a handle (used when referencing the group in queries and templates);
- …the maximum number of levels categories can be nested, within the group;
- …the format of category URIs used for routing;
- …which template should be rendered when a category’s URL is accessed;
- …which fields categories in the group should have;
To create a new category group, go to
- Settings
- Categories
#Category Field Layout
Each category group has its own field layout, which allows you to customize the data that’s associated with each category in the group. By default, categories only have a Title and Slug, but you can add as many other custom fields as necessary to satisfy your content architecture.
#Creating and Editing Categories
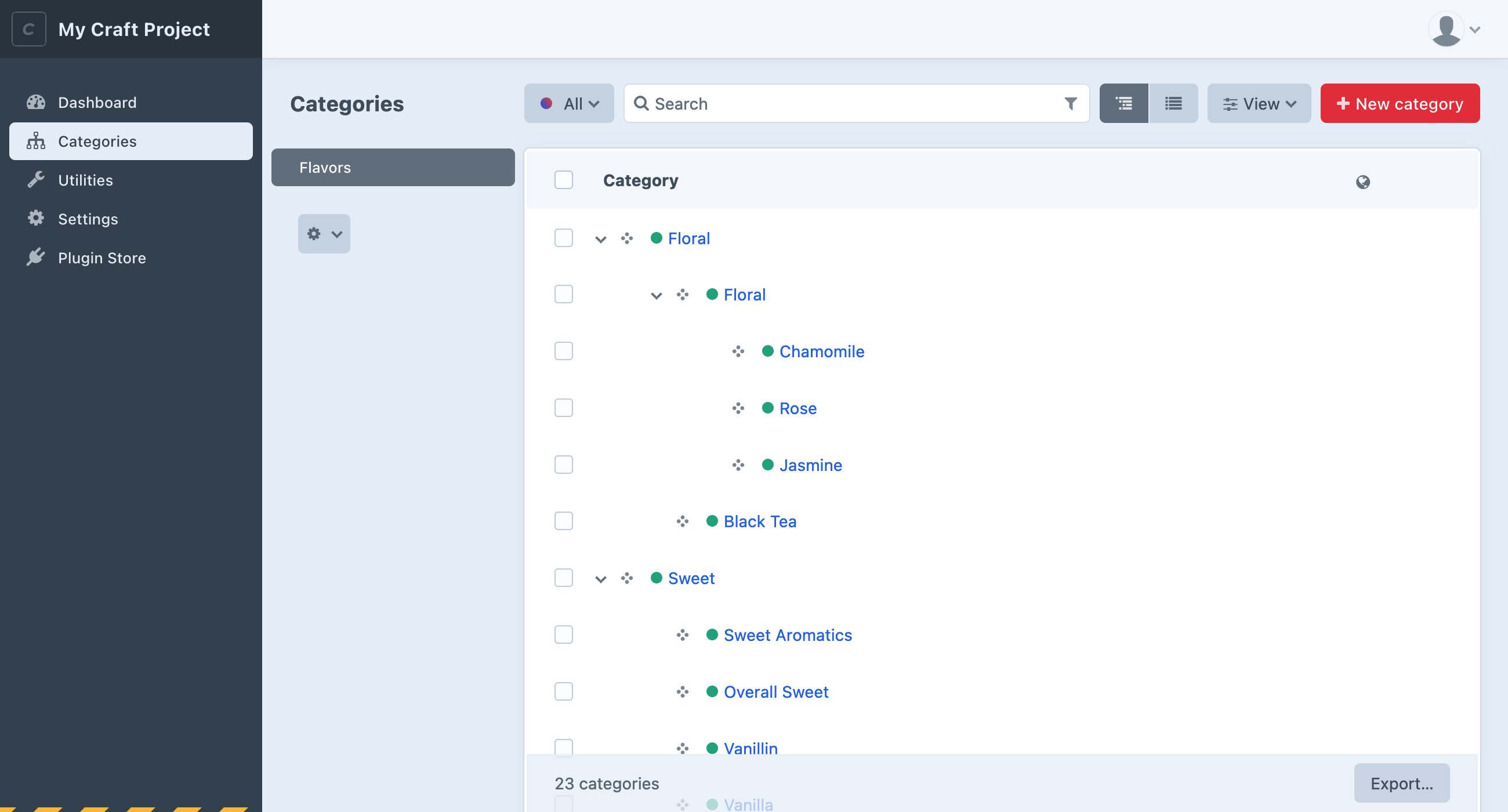
When you’ve defined at least one category group, Categories will appear in the control panel’s primary navigation. Clicking it will take you to the category index. From there, you can choose a category group from the sidebar, and add/reorder/delete categories within it:
Select the “Structure” sort option to view and manipulate the categories’ hierarchy. Double-click any element to open a slideout.
You can also click a category’s title to visit its edit page just like an entry.
When you create a category, you have the following options:
- Fill out the category fields (if you didn’t define any, the only field available will be Title)
- Edit the slug (it’s automatically populated based on the title).
- Choose a Parent category. The new category will have a hierarchical relationship with its parent. This is helpful for creating taxonomies with multiple levels. You also have the option of creating a new category while assigning the Parent.
You can only nest categories up to the level specified in the Max Level field Category Group settings. By default, there is no limit to how deeply-nested categories can be.
#Assigning Categories
To assign categories to things (entries, assets, users, etc.), you must first create a categories field.
Each Categories field is connected to a single category group. Whatever you attach the field to will store relations to categories selected from that group.
#Routing and Templates
Category groups’ URI Format setting is equivalent to that of entries, so any of the object template strategies discussed in this section apply to categories, as well.
When a category’s URL is requested, Craft renders the template defined by its group, and makes a special category variable available. Supposing a Flavors category group had a URI Format of flavors/{slug} and was configured to use _categories/flavors.twig as its Template:
{{ category.title }}
{# -> "Sour Aromatics" #}
{{ category.ancestors.collect()
.select('title')
.join(' / ') }}
{# -> "Sour & Fermented / Sour" #}
Custom fields attached to the group’s field layout are also available via the category variable.
#Querying Categories
You can fetch categories in your templates or PHP code using category queries.
{# Create a new category query #}
{% set myCategoryQuery = craft.categories() %}
// Create a new category query
$myCategoryQuery = \craft\elements\Category::find();
Once you’ve created a category query, you can set parameters on it to narrow down the results, and then execute it by calling .all(). An array of Category (opens new window) objects will be returned.
#Example
We can display a navigation for all the categories in a Flavors category group by doing the following:
- Create a category query with
craft.categories(). - Set the group parameter on it using its handle.
- Fetch the categories with
.all(). - Loop through the categories using a nav tag to create the navigation HTML.
{# Create a category query with the 'group' parameter #}
{% set myCategoryQuery = craft.categories()
.group('flavors') %}
{# Fetch the categories #}
{% set categories = myCategoryQuery.all() %}
{# Display the navigation #}
<ul>
{% nav category in categories %}
<li>
<a href="{{ category.url }}">{{ category.title }}</a>
{% ifchildren %}
<ul>
{% children %}
</ul>
{% endifchildren %}
</li>
{% endnav %}
</ul>
Keep in mind that this only holds value for category groups with multiple hierarchical levels. If you were working with a “flat” taxonomy, the template above should use a regular {% for %} tag in lieu of Craft’s {% nav %} tag.
To maintain the exact order you see in the control panel, add orderBy('lft ASC') to your query:
{% set myCategoryQuery = craft.categories()
.group('flavors')
.orderBy('lft ASC') %}
#Elements Related to a Category
When you’ve attached a categories field to another type of element, you can query for those elements when you have a reference to a category.
For example, if we were building a “Tasting Notes” database with dedicated Flavor (category) pages, we might build a query like this to look up records:
{% set records = craft.entries()
.relatedTo({
targetElement: category,
field: 'flavors',
})
.all() %}
Here, flavors also happens to be the handle of the relational field. You do not need to follow any kind of convention when naming relational fields; the groups available for selection in a given categories field are explicitly defined on that field.
You can also use the field’s query method to set up the relational constraint, automatically:
{% set records = craft.entries()
.flavors(category)
.all() %}
In both cases, we’re assuming the category variable comes from Craft, when loading an individual category’s template.
#Parameters
Category queries support the following parameters:
| Param | Description |
|---|---|
| ancestorDist | Narrows the query results to only categories that are up to a certain distance away from the category specified by ancestorOf. |
| ancestorOf | Narrows the query results to only categories that are ancestors of another category in its structure. |
| andNotRelatedTo | Narrows the query results to only categories that are not related to certain other elements. |
| andRelatedTo | Narrows the query results to only categories that are related to certain other elements. |
| andWith | Causes the query to return matching categories eager-loaded with related elements, in addition to the elements that were already specified by with. |
| asArray | Causes the query to return matching categories as arrays of data, rather than Category (opens new window) objects. |
| cache | Enables query cache for this Query. |
| canonicalsOnly | Narrows the query results to only canonical elements, including elements that reference another canonical element via canonicalId so long as they aren’t a draft. |
| clearCachedResult | Clears the cached result (opens new window). |
| dateCreated | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ creation dates. |
| dateUpdated | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ last-updated dates. |
| descendantDist | Narrows the query results to only categories that are up to a certain distance away from the category specified by descendantOf. |
| descendantOf | Narrows the query results to only categories that are descendants of another category in its structure. |
| eagerly | Causes the query to be used to eager-load results for the query’s source element and any other elements in its collection. |
| fixedOrder | Causes the query results to be returned in the order specified by id. |
| getFieldLayouts | Returns the field layouts that could be associated with the resulting elements. |
| group | Narrows the query results based on the category groups the categories belong to. |
| groupId | Narrows the query results based on the category groups the categories belong to, per the groups’ IDs. |
| hasDescendants | Narrows the query results based on whether the categories have any descendants in their structure. |
| id | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ IDs. |
| ignorePlaceholders | Causes the query to return matching categories as they are stored in the database, ignoring matching placeholder elements that were set by craft\services\Elements::setPlaceholderElement() (opens new window). |
| inBulkOp | Narrows the query results to only categories that were involved in a bulk element operation. |
| inReverse | Causes the query results to be returned in reverse order. |
| language | Determines which site(s) the categories should be queried in, based on their language. |
| leaves | Narrows the query results based on whether the categories are “leaves” (categories with no descendants). |
| level | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ level within the structure. |
| limit | Determines the number of categories that should be returned. |
| nextSiblingOf | Narrows the query results to only the category that comes immediately after another category in its structure. |
| notRelatedTo | Narrows the query results to only categories that are not related to certain other elements. |
| offset | Determines how many categories should be skipped in the results. |
| orderBy | Determines the order that the categories should be returned in. (If empty, defaults to dateCreated DESC, elements.id, or the order defined by the category group if the group or groupId params are set to a single group.) |
| positionedAfter | Narrows the query results to only categories that are positioned after another category in its structure. |
| positionedBefore | Narrows the query results to only categories that are positioned before another category in its structure. |
| preferSites | If unique is set, this determines which site should be selected when querying multi-site elements. |
| prepForEagerLoading | Prepares the query for lazy eager loading. |
| prepareSubquery | Prepares the element query and returns its subquery (which determines what elements will be returned). |
| prevSiblingOf | Narrows the query results to only the category that comes immediately before another category in its structure. |
| relatedTo | Narrows the query results to only categories that are related to certain other elements. |
| render | Executes the query and renders the resulting elements using their partial templates. |
| search | Narrows the query results to only categories that match a search query. |
| siblingOf | Narrows the query results to only categories that are siblings of another category in its structure. |
| site | Determines which site(s) the categories should be queried in. |
| siteId | Determines which site(s) the categories should be queried in, per the site’s ID. |
| siteSettingsId | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ IDs in the elements_sites table. |
| slug | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ slugs. |
| status | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ statuses. |
| title | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ titles. |
| trashed | Narrows the query results to only categories that have been soft-deleted. |
| uid | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ UIDs. |
| unique | Determines whether only elements with unique IDs should be returned by the query. |
| uri | Narrows the query results based on the categories’ URIs. |
| wasCountEagerLoaded | Returns whether the query result count was already eager loaded by the query's source element. |
| wasEagerLoaded | Returns whether the query results were already eager loaded by the query's source element. |
| with | Causes the query to return matching categories eager-loaded with related elements. |
| withCustomFields | Sets whether custom fields should be factored into the query. |
| withProvisionalDrafts | Causes the query to return provisional drafts for the matching elements, when they exist for the current user. |
#ancestorDist
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are up to a certain distance away from the category specified by ancestorOf.
{# Fetch categories above this one #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.ancestorOf(myCategory)
.ancestorDist(3)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories above this one
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->ancestorOf($myCategory)
->ancestorDist(3)
->all();
#ancestorOf
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are ancestors of another category in its structure.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | above the category with an ID of 1. |
| a Category (opens new window) object | above the category represented by the object. |
{# Fetch categories above this one #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.ancestorOf(myCategory)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories above this one
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->ancestorOf($myCategory)
->all();
This can be combined with ancestorDist if you want to limit how far away the ancestor categories can be.
#andNotRelatedTo
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are not related to certain other elements.
See Relations (opens new window) for a full explanation of how to work with this parameter.
{# Fetch all categories that are related to myCategoryA and not myCategoryB #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.relatedTo(myCategoryA)
.andNotRelatedTo(myCategoryB)
.all() %}
// Fetch all categories that are related to $myCategoryA and not $myCategoryB
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->relatedTo($myCategoryA)
->andNotRelatedTo($myCategoryB)
->all();
#andRelatedTo
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are related to certain other elements.
See Relations (opens new window) for a full explanation of how to work with this parameter.
{# Fetch all categories that are related to myCategoryA and myCategoryB #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.relatedTo(myCategoryA)
.andRelatedTo(myCategoryB)
.all() %}
// Fetch all categories that are related to $myCategoryA and $myCategoryB
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->relatedTo($myCategoryA)
->andRelatedTo($myCategoryB)
->all();
#andWith
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Causes the query to return matching categories eager-loaded with related elements, in addition to the elements that were already specified by with.
.
#asArray
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Causes the query to return matching categories as arrays of data, rather than Category (opens new window) objects.
{# Fetch categories as arrays #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.asArray()
.all() %}
// Fetch categories as arrays
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->asArray()
->all();
#cache
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Enables query cache for this Query.
#canonicalsOnly
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only canonical elements, including elements
that reference another canonical element via canonicalId so long as they
aren’t a draft.
Unpublished drafts can be included as well if drafts(null) and
draftOf(false) are also passed.
#clearCachedResult
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Clears the cached result (opens new window).
#dateCreated
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ creation dates.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'>= 2018-04-01' | that were created on or after 2018-04-01. |
'< 2018-05-01' | that were created before 2018-05-01. |
['and', '>= 2018-04-04', '< 2018-05-01'] | that were created between 2018-04-01 and 2018-05-01. |
now/today/tomorrow/yesterday | that were created at midnight of the specified relative date. |
{# Fetch categories created last month #}
{% set start = date('first day of last month')|atom %}
{% set end = date('first day of this month')|atom %}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.dateCreated(['and', ">= #{start}", "< #{end}"])
.all() %}
// Fetch categories created last month
$start = (new \DateTime('first day of last month'))->format(\DateTime::ATOM);
$end = (new \DateTime('first day of this month'))->format(\DateTime::ATOM);
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->dateCreated(['and', ">= {$start}", "< {$end}"])
->all();
#dateUpdated
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ last-updated dates.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'>= 2018-04-01' | that were updated on or after 2018-04-01. |
'< 2018-05-01' | that were updated before 2018-05-01. |
['and', '>= 2018-04-04', '< 2018-05-01'] | that were updated between 2018-04-01 and 2018-05-01. |
now/today/tomorrow/yesterday | that were updated at midnight of the specified relative date. |
{# Fetch categories updated in the last week #}
{% set lastWeek = date('1 week ago')|atom %}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.dateUpdated(">= #{lastWeek}")
.all() %}
// Fetch categories updated in the last week
$lastWeek = (new \DateTime('1 week ago'))->format(\DateTime::ATOM);
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->dateUpdated(">= {$lastWeek}")
->all();
#descendantDist
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are up to a certain distance away from the category specified by descendantOf.
{# Fetch categories below this one #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.descendantOf(myCategory)
.descendantDist(3)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories below this one
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->descendantOf($myCategory)
->descendantDist(3)
->all();
#descendantOf
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are descendants of another category in its structure.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | below the category with an ID of 1. |
| a Category (opens new window) object | below the category represented by the object. |
{# Fetch categories below this one #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.descendantOf(myCategory)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories below this one
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->descendantOf($myCategory)
->all();
This can be combined with descendantDist if you want to limit how far away the descendant categories can be.
#eagerly
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Causes the query to be used to eager-load results for the query’s source element and any other elements in its collection.
#fixedOrder
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Causes the query results to be returned in the order specified by id.
If no IDs were passed to id, setting this to true will result in an empty result set.
{# Fetch categories in a specific order #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.id([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
.fixedOrder()
.all() %}
// Fetch categories in a specific order
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->id([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
->fixedOrder()
->all();
#getFieldLayouts
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Returns the field layouts that could be associated with the resulting elements.
#group
Narrows the query results based on the category groups the categories belong to.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'foo' | in a group with a handle of foo. |
'not foo' | not in a group with a handle of foo. |
['foo', 'bar'] | in a group with a handle of foo or bar. |
['not', 'foo', 'bar'] | not in a group with a handle of foo or bar. |
| a CategoryGroup (opens new window) object | in a group represented by the object. |
{# Fetch categories in the Foo group #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.group('foo')
.all() %}
// Fetch categories in the Foo group
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->group('foo')
->all();
#groupId
Narrows the query results based on the category groups the categories belong to, per the groups’ IDs.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | in a group with an ID of 1. |
'not 1' | not in a group with an ID of 1. |
[1, 2] | in a group with an ID of 1 or 2. |
['not', 1, 2] | not in a group with an ID of 1 or 2. |
{# Fetch categories in the group with an ID of 1 #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.groupId(1)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories in the group with an ID of 1
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->groupId(1)
->all();
#hasDescendants
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on whether the categories have any descendants in their structure.
(This has the opposite effect of calling leaves.)
{# Fetch categories that have descendants #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.hasDescendants()
.all() %}
// Fetch categories that have descendants
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->hasDescendants()
->all();
#id
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ IDs.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | with an ID of 1. |
'not 1' | not with an ID of 1. |
[1, 2] | with an ID of 1 or 2. |
['not', 1, 2] | not with an ID of 1 or 2. |
{# Fetch the category by its ID #}
{% set category = craft.categories()
.id(1)
.one() %}
// Fetch the category by its ID
$category = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->id(1)
->one();
This can be combined with fixedOrder if you want the results to be returned in a specific order.
#ignorePlaceholders
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Causes the query to return matching categories as they are stored in the database, ignoring matching placeholder elements that were set by craft\services\Elements::setPlaceholderElement() (opens new window).
#inBulkOp
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that were involved in a bulk element operation.
#inReverse
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Causes the query results to be returned in reverse order.
{# Fetch categories in reverse #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.inReverse()
.all() %}
// Fetch categories in reverse
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->inReverse()
->all();
#language
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Determines which site(s) the categories should be queried in, based on their language.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'en' | from sites with a language of en. |
['en-GB', 'en-US'] | from sites with a language of en-GB or en-US. |
['not', 'en-GB', 'en-US'] | not in sites with a language of en-GB or en-US. |
Elements that belong to multiple sites will be returned multiple times by default. If you only want unique elements to be returned, use unique in conjunction with this.
{# Fetch categories from English sites #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.language('en')
.all() %}
// Fetch categories from English sites
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->language('en')
->all();
#leaves
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on whether the categories are “leaves” (categories with no descendants).
(This has the opposite effect of calling hasDescendants.)
{# Fetch categories that have no descendants #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.leaves()
.all() %}
// Fetch categories that have no descendants
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->leaves()
->all();
#level
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ level within the structure.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | with a level of 1. |
'not 1' | not with a level of 1. |
'>= 3' | with a level greater than or equal to 3. |
[1, 2] | with a level of 1 or 2. |
[null, 1] | without a level, or a level of 1. |
['not', 1, 2] | not with level of 1 or 2. |
{# Fetch categories positioned at level 3 or above #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.level('>= 3')
.all() %}
// Fetch categories positioned at level 3 or above
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->level('>= 3')
->all();
#limit
Determines the number of categories that should be returned.
{# Fetch up to 10 categories #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.limit(10)
.all() %}
// Fetch up to 10 categories
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->limit(10)
->all();
#nextSiblingOf
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only the category that comes immediately after another category in its structure.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches the category… |
|---|---|
1 | after the category with an ID of 1. |
| a Category (opens new window) object | after the category represented by the object. |
{# Fetch the next category #}
{% set category = craft.categories()
.nextSiblingOf(myCategory)
.one() %}
// Fetch the next category
$category = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->nextSiblingOf($myCategory)
->one();
#notRelatedTo
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are not related to certain other elements.
See Relations (opens new window) for a full explanation of how to work with this parameter.
{# Fetch all categories that are related to myEntry #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.notRelatedTo(myEntry)
.all() %}
// Fetch all categories that are related to $myEntry
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->notRelatedTo($myEntry)
->all();
#offset
Determines how many categories should be skipped in the results.
{# Fetch all categories except for the first 3 #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.offset(3)
.all() %}
// Fetch all categories except for the first 3
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->offset(3)
->all();
#orderBy
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Determines the order that the categories should be returned in. (If empty, defaults to dateCreated DESC, elements.id, or the order defined by the category group if the group or groupId params are set to a single group.)
{# Fetch all categories in order of date created #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.orderBy('dateCreated ASC')
.all() %}
// Fetch all categories in order of date created
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->orderBy('dateCreated ASC')
->all();
#positionedAfter
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are positioned after another category in its structure.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | after the category with an ID of 1. |
| a Category (opens new window) object | after the category represented by the object. |
{# Fetch categories after this one #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.positionedAfter(myCategory)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories after this one
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->positionedAfter($myCategory)
->all();
#positionedBefore
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are positioned before another category in its structure.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | before the category with an ID of 1. |
| a Category (opens new window) object | before the category represented by the object. |
{# Fetch categories before this one #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.positionedBefore(myCategory)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories before this one
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->positionedBefore($myCategory)
->all();
#preferSites
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
If unique is set, this determines which site should be selected when querying multi-site elements.
For example, if element “Foo” exists in Site A and Site B, and element “Bar” exists in Site B and Site C,
and this is set to ['c', 'b', 'a'], then Foo will be returned for Site B, and Bar will be returned
for Site C.
If this isn’t set, then preference goes to the current site.
{# Fetch unique categories from Site A, or Site B if they don’t exist in Site A #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.site('*')
.unique()
.preferSites(['a', 'b'])
.all() %}
// Fetch unique categories from Site A, or Site B if they don’t exist in Site A
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->site('*')
->unique()
->preferSites(['a', 'b'])
->all();
#prepForEagerLoading
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Prepares the query for lazy eager loading.
#prepareSubquery
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Prepares the element query and returns its subquery (which determines what elements will be returned).
#prevSiblingOf
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only the category that comes immediately before another category in its structure.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches the category… |
|---|---|
1 | before the category with an ID of 1. |
| a Category (opens new window) object | before the category represented by the object. |
{# Fetch the previous category #}
{% set category = craft.categories()
.prevSiblingOf(myCategory)
.one() %}
// Fetch the previous category
$category = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->prevSiblingOf($myCategory)
->one();
#relatedTo
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are related to certain other elements.
See Relations (opens new window) for a full explanation of how to work with this parameter.
{# Fetch all categories that are related to myCategory #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.relatedTo(myCategory)
.all() %}
// Fetch all categories that are related to $myCategory
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->relatedTo($myCategory)
->all();
#render
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Executes the query and renders the resulting elements using their partial templates.
If no partial template exists for an element, its string representation will be output instead.
#search
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that match a search query.
See Searching (opens new window) for a full explanation of how to work with this parameter.
{# Get the search query from the 'q' query string param #}
{% set searchQuery = craft.app.request.getQueryParam('q') %}
{# Fetch all categories that match the search query #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.search(searchQuery)
.all() %}
// Get the search query from the 'q' query string param
$searchQuery = \Craft::$app->request->getQueryParam('q');
// Fetch all categories that match the search query
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->search($searchQuery)
->all();
#siblingOf
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that are siblings of another category in its structure.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | beside the category with an ID of 1. |
| a Category (opens new window) object | beside the category represented by the object. |
{# Fetch categories beside this one #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.siblingOf(myCategory)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories beside this one
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->siblingOf($myCategory)
->all();
#site
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Determines which site(s) the categories should be queried in.
The current site will be used by default.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'foo' | from the site with a handle of foo. |
['foo', 'bar'] | from a site with a handle of foo or bar. |
['not', 'foo', 'bar'] | not in a site with a handle of foo or bar. |
| a craft\models\Site (opens new window) object | from the site represented by the object. |
'*' | from any site. |
If multiple sites are specified, elements that belong to multiple sites will be returned multiple times. If you only want unique elements to be returned, use unique in conjunction with this.
{# Fetch categories from the Foo site #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.site('foo')
.all() %}
// Fetch categories from the Foo site
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->site('foo')
->all();
#siteId
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Determines which site(s) the categories should be queried in, per the site’s ID.
The current site will be used by default.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | from the site with an ID of 1. |
[1, 2] | from a site with an ID of 1 or 2. |
['not', 1, 2] | not in a site with an ID of 1 or 2. |
'*' | from any site. |
{# Fetch categories from the site with an ID of 1 #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.siteId(1)
.all() %}
// Fetch categories from the site with an ID of 1
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->siteId(1)
->all();
#siteSettingsId
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ IDs in the elements_sites table.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
1 | with an elements_sites ID of 1. |
'not 1' | not with an elements_sites ID of 1. |
[1, 2] | with an elements_sites ID of 1 or 2. |
['not', 1, 2] | not with an elements_sites ID of 1 or 2. |
{# Fetch the category by its ID in the elements_sites table #}
{% set category = craft.categories()
.siteSettingsId(1)
.one() %}
// Fetch the category by its ID in the elements_sites table
$category = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->siteSettingsId(1)
->one();
#slug
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ slugs.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'foo' | with a slug of foo. |
'foo*' | with a slug that begins with foo. |
'*foo' | with a slug that ends with foo. |
'*foo*' | with a slug that contains foo. |
'not *foo*' | with a slug that doesn’t contain foo. |
['*foo*', '*bar*'] | with a slug that contains foo or bar. |
['not', '*foo*', '*bar*'] | with a slug that doesn’t contain foo or bar. |
{# Get the requested category slug from the URL #}
{% set requestedSlug = craft.app.request.getSegment(3) %}
{# Fetch the category with that slug #}
{% set category = craft.categories()
.slug(requestedSlug|literal)
.one() %}
// Get the requested category slug from the URL
$requestedSlug = \Craft::$app->request->getSegment(3);
// Fetch the category with that slug
$category = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->slug(\craft\helpers\Db::escapeParam($requestedSlug))
->one();
#status
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ statuses.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'enabled' (default) | that are enabled. |
'disabled' | that are disabled. |
['not', 'disabled'] | that are not disabled. |
{# Fetch disabled categories #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.status('disabled')
.all() %}
// Fetch disabled categories
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->status('disabled')
->all();
#title
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ titles.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'Foo' | with a title of Foo. |
'Foo*' | with a title that begins with Foo. |
'*Foo' | with a title that ends with Foo. |
'*Foo*' | with a title that contains Foo. |
'not *Foo*' | with a title that doesn’t contain Foo. |
['*Foo*', '*Bar*'] | with a title that contains Foo or Bar. |
['not', '*Foo*', '*Bar*'] | with a title that doesn’t contain Foo or Bar. |
{# Fetch categories with a title that contains "Foo" #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.title('*Foo*')
.all() %}
// Fetch categories with a title that contains "Foo"
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->title('*Foo*')
->all();
#trashed
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results to only categories that have been soft-deleted.
{# Fetch trashed categories #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.trashed()
.all() %}
// Fetch trashed categories
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->trashed()
->all();
#uid
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ UIDs.
{# Fetch the category by its UID #}
{% set category = craft.categories()
.uid('xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx')
.one() %}
// Fetch the category by its UID
$category = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->uid('xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx')
->one();
#unique
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Determines whether only elements with unique IDs should be returned by the query.
This should be used when querying elements from multiple sites at the same time, if “duplicate” results is not desired.
{# Fetch unique categories across all sites #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.site('*')
.unique()
.all() %}
// Fetch unique categories across all sites
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->site('*')
->unique()
->all();
#uri
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Narrows the query results based on the categories’ URIs.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches categories… |
|---|---|
'foo' | with a URI of foo. |
'foo*' | with a URI that begins with foo. |
'*foo' | with a URI that ends with foo. |
'*foo*' | with a URI that contains foo. |
'not *foo*' | with a URI that doesn’t contain foo. |
['*foo*', '*bar*'] | with a URI that contains foo or bar. |
['not', '*foo*', '*bar*'] | with a URI that doesn’t contain foo or bar. |
{# Get the requested URI #}
{% set requestedUri = craft.app.request.getPathInfo() %}
{# Fetch the category with that URI #}
{% set category = craft.categories()
.uri(requestedUri|literal)
.one() %}
// Get the requested URI
$requestedUri = \Craft::$app->request->getPathInfo();
// Fetch the category with that URI
$category = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->uri(\craft\helpers\Db::escapeParam($requestedUri))
->one();
#wasCountEagerLoaded
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Returns whether the query result count was already eager loaded by the query's source element.
#wasEagerLoaded
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Returns whether the query results were already eager loaded by the query's source element.
#with
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Causes the query to return matching categories eager-loaded with related elements.
See Eager-Loading Elements (opens new window) for a full explanation of how to work with this parameter.
{# Fetch categories eager-loaded with the "Related" field’s relations #}
{% set categories = craft.categories()
.with(['related'])
.all() %}
// Fetch categories eager-loaded with the "Related" field’s relations
$categories = \craft\elements\Category::find()
->with(['related'])
->all();
#withCustomFields
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Sets whether custom fields should be factored into the query.
#withProvisionalDrafts
Defined by craft\elements\db\ElementQuery
Causes the query to return provisional drafts for the matching elements, when they exist for the current user.