Matrix Fields
Matrix fields allow you to manage nested entries in a fluid way. Entries created within a Matrix field are “owned” by the element the field is attached to, and can represent anything from a slide in a gallery to an entire resource library, each record having its own URL.
During the Craft 5 upgrade, Matrix blocks were converted to entries. Fields that were previously owned by a particular “block type” are now managed in (and assigned from) a global pool. You are now able to design entry types that exist as standalone content objects (in a section), or as nested entries (in a Matrix field)!
#Settings
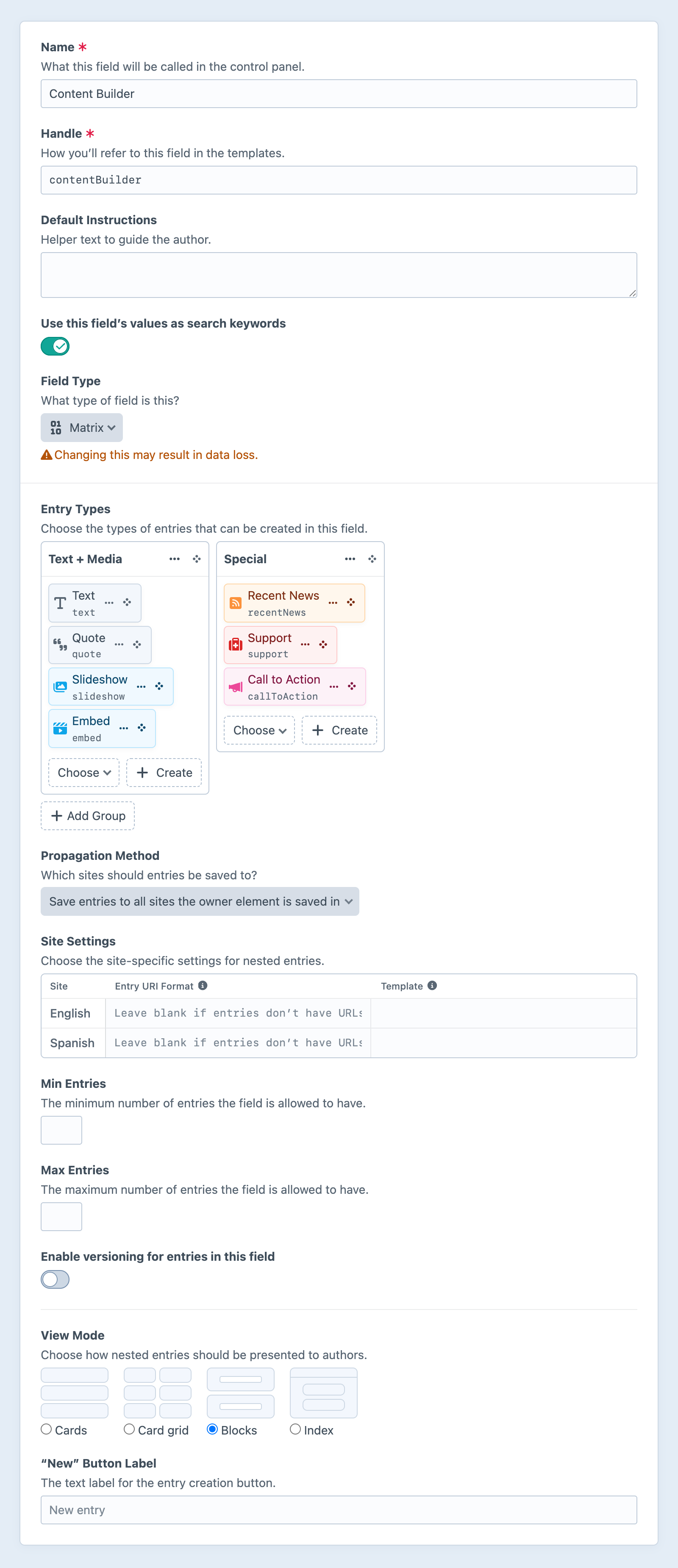
#Entry Types
Select from existing, globally-defined entry types, or create a new one on-the-fly.
You can specify local overrides for each attached entry type’s Name and Handle by selecting Settings from a chip’s action
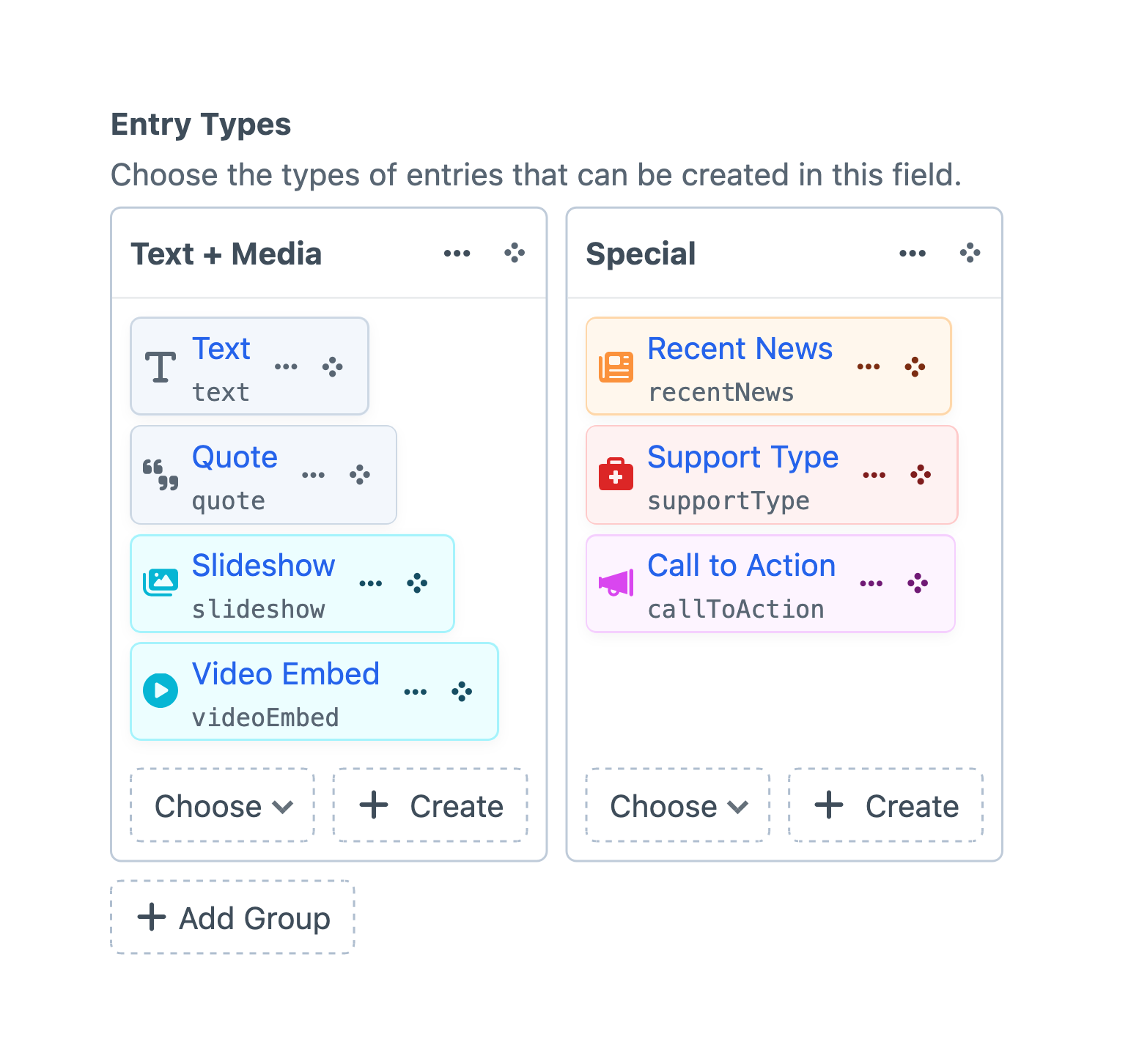
#Groups 5.8.0+
Entry types are organized into named groups. Groups affect the structure of the menu (or menus, when horizontal space allows 5.9.0+) displayed to authors.
#Propagation Method
Choose how nested entries are propagated to other sites. This applies only to new nested entries—changes to existing nested entries are propagated on a per-field basis.
#Site Settings New!
Nested entries can have their own URLs and templates.
Incorporate the owner’s URI in a nested element by using {owner.uri} in its URI Format object template!
#Min Entries
The minimum number of entries that can be created within the field. (Default is no lower limit.)
#Max Entries
The maximum number of entries that can be created within the field. (Default is no upper limit.)
#Versioning 5.7.0+
Nested entries using the As inline-editable blocks view mode are “versioned” alongside their owner: when making a change directly within the context of the owner, Craft automatically creates revisions for both elements. Those revisions are only exposed via the control panel; they are only returned in the front-end when explicitly requested (or as part of a preview request).
The Enable versioning for entries in this field setting exposes the revisions menu and the Notes field in the sidebar, when editing a nested entry in its own screen.
#View Mode New!

Choose how the nested elements are represented within the field UI:
- Cards: Read-only element cards that surface nested field data.
- Card grid: Similar to As cards, but cards are limited in width and arranged in a grid. 5.9.0+
- Blocks: Manage nested entries as though they were part of the current element. Historically, this was the only display option for Matrix fields.
- Index: A simplified element index with sorting, searching, and filtering controls.
This view mode includes additional options:
- Include Table View: Allow authors to toggle between the default card view and a traditional table view.
- Default Table Columns: Select which attributes and fields are visible when using the table mode. (To change what attributes are displayed on cards, refer to that entry type’s settings.)
- Default View Mode: Set the default presentation of elements in the index. Authors can always switch between them, later.
- Include Table View: Allow authors to toggle between the default card view and a traditional table view.
Some settings were consolidated into View Mode controls in 5.9.0 (opens new window). Prior, the As cards view mode had a nested setting that controlled whether the cards were stacked or presented in a grid.
#“New” Button Label
This setting only applies when there is not enough horizontal space to display a button per group of entry types. When grouped, each button uses its group’s label.
By default, the button authors use to create nested entries will be labeled New entry. You can override this label with one that better suits the intended content.
#The Field
The interface of a Matrix field depends on its selected view mode.
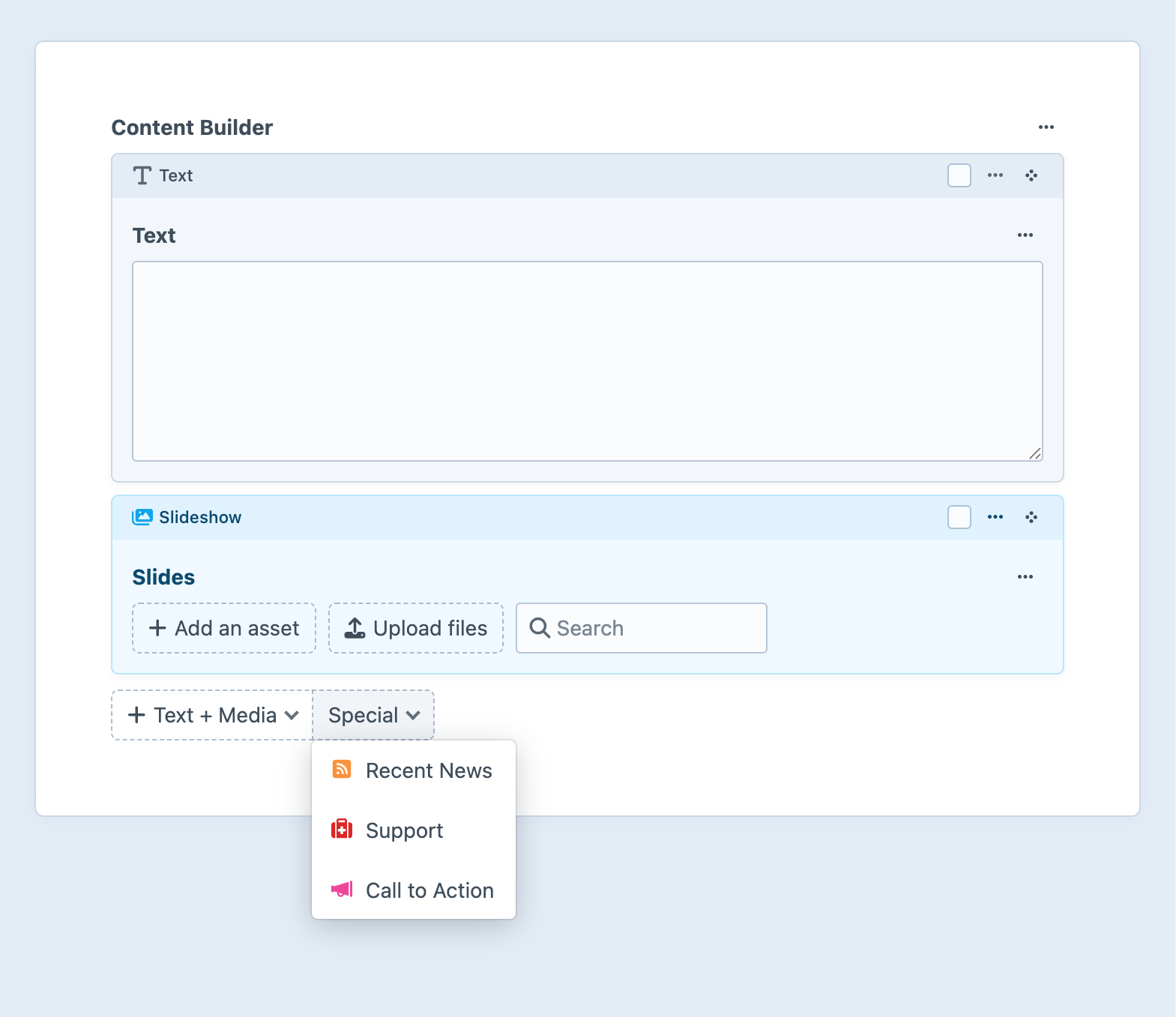
Traditionally, Matrix fields have used the Blocks view mode, which makes the nested entries appear as though they are a repeating or modular region the main element’s form. An empty Matrix field shows one or more buttons, which will either immediately create a new nested entry (if there is only a single available entry type), or present a menu of entry types to select from:
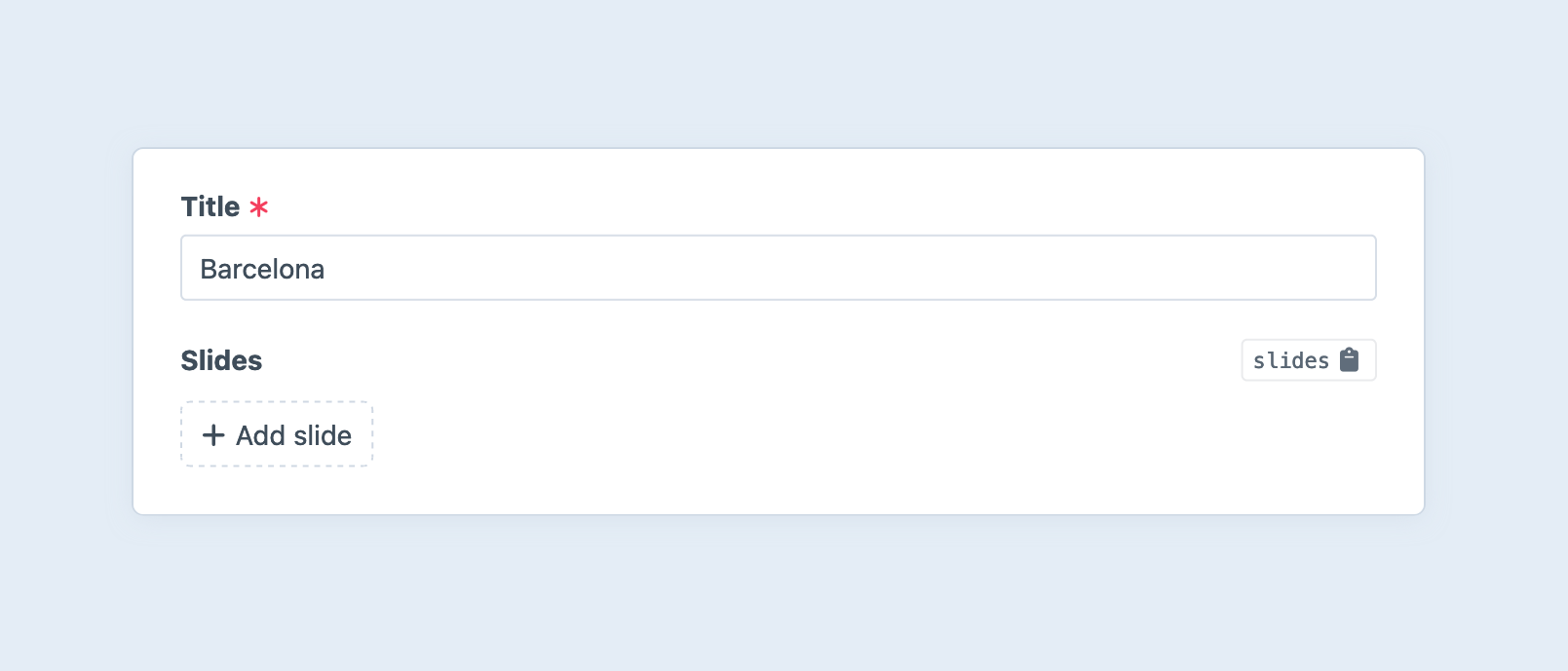
A new entry of the chosen type will be appended to the list:
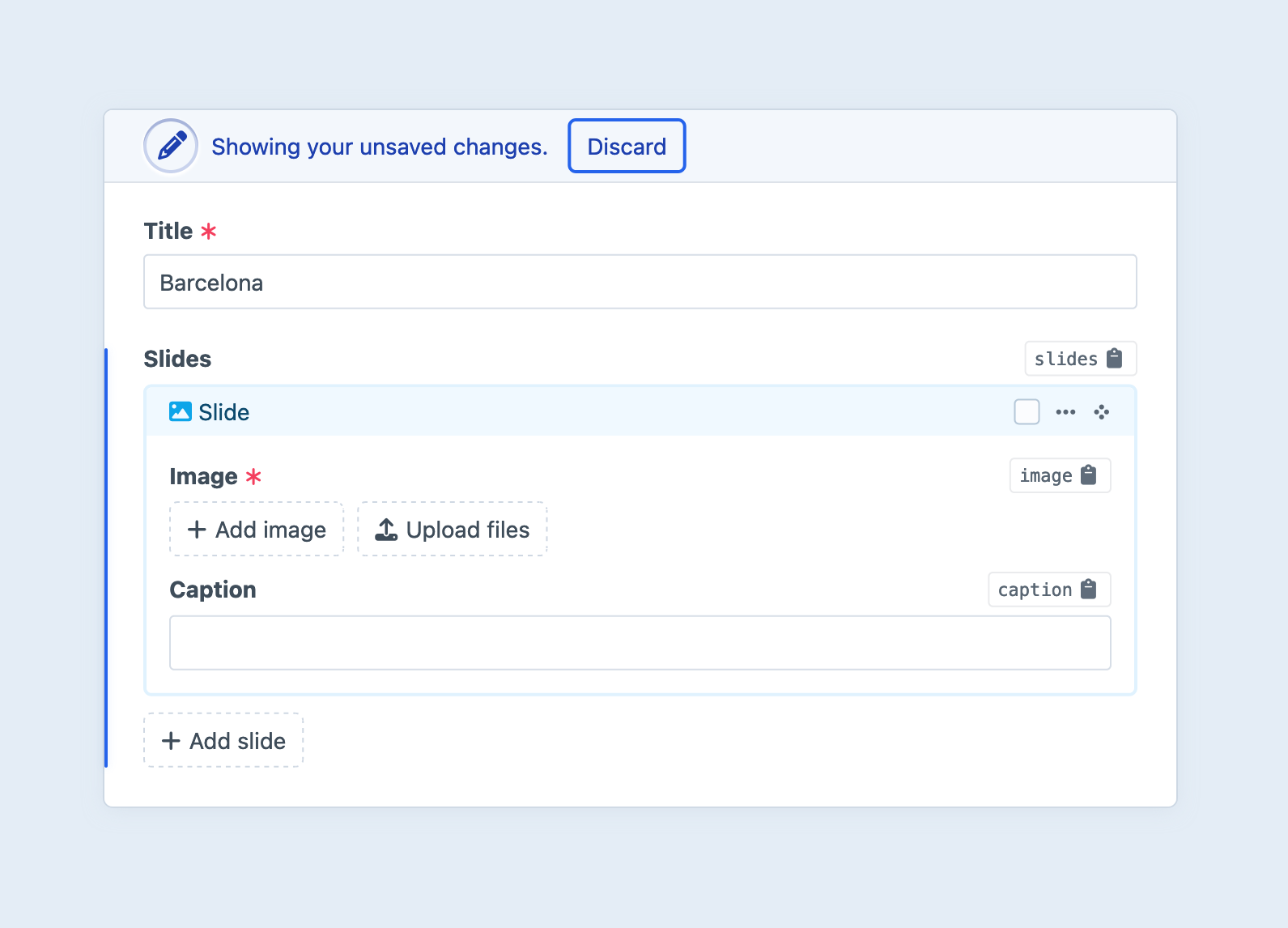
You can add as many nested entries to your Matrix field as you’d like (as long as it’s between the field’s Min Entries and Max Entries settings).
#Actions
Each block (or card) has a menu that provides access to additional controls, depending on the context…
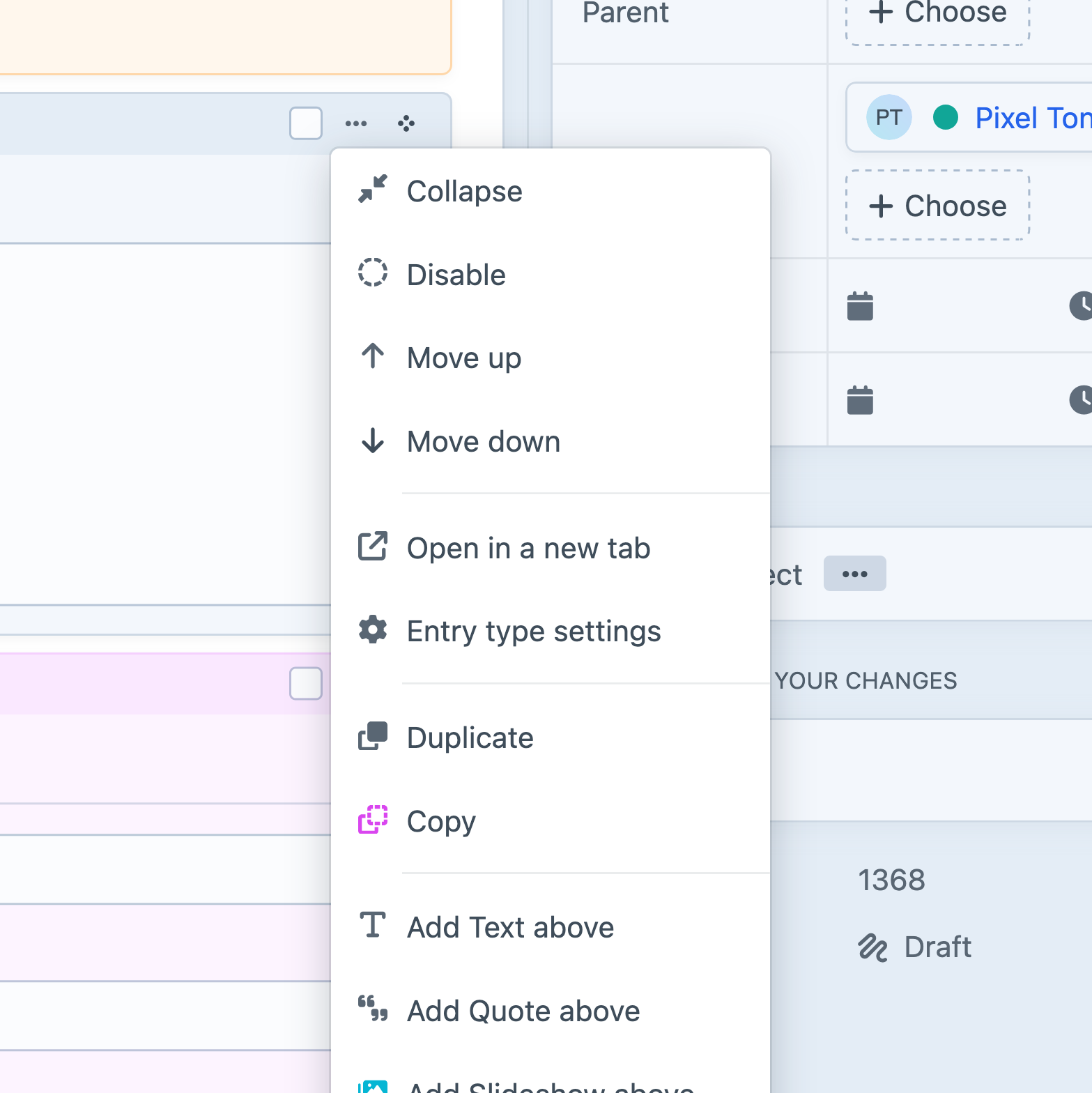
…and the Matrix field itself includes options to Collapse all/selected blocks 5.8.0+ and Copy all/selected entries:
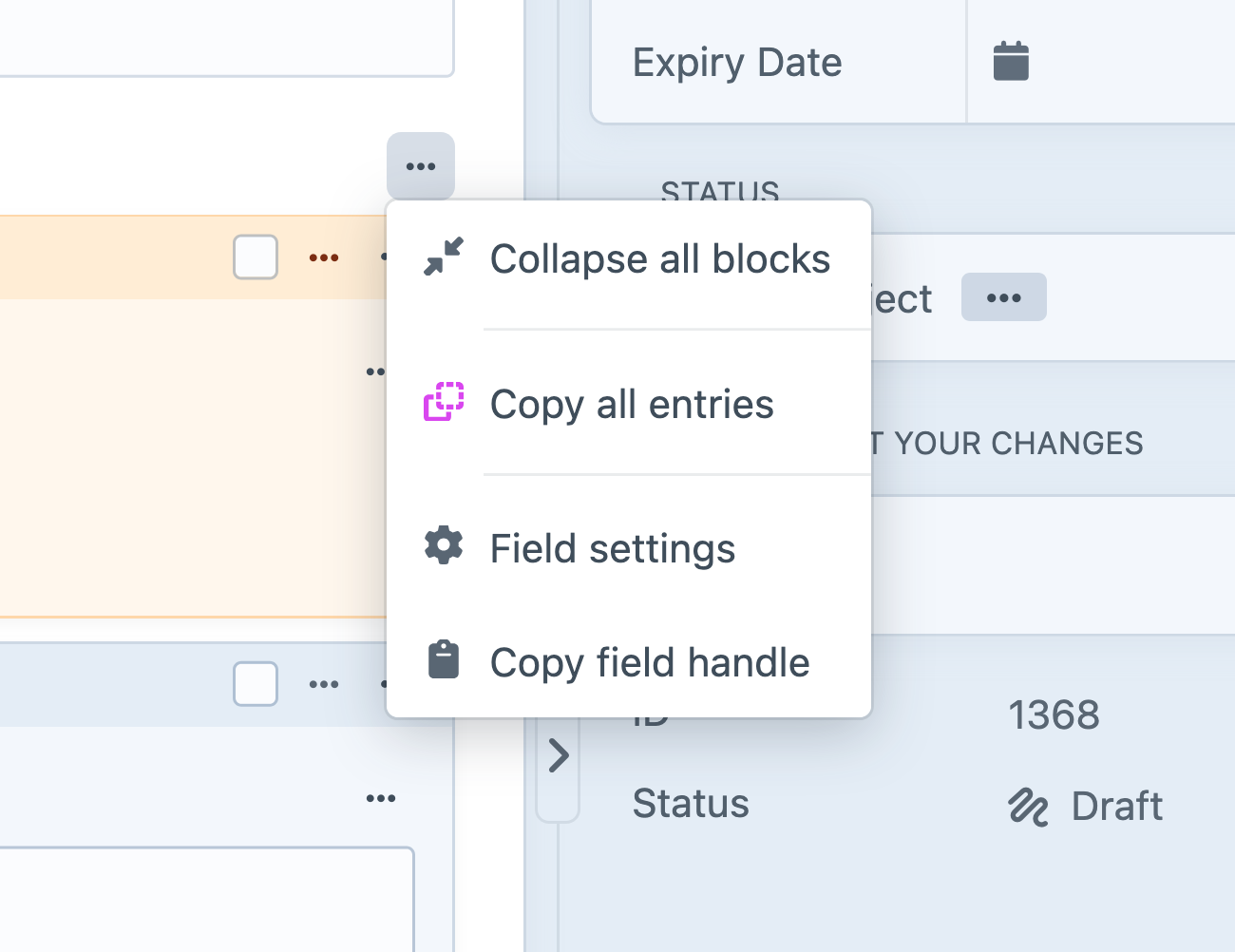
If multiple nested entries are selected, the Collapse/Expand, Disable/Enable, and Delete options will apply to each of them.
You can collapse inline Matrix blocks by choosing the Collapse menu option or by double-clicking on a block’s title bar. When a block is collapsed, its title bar will show a preview of its content so you can still identify which block it is.
Inline-blocks can also be reordered by dragging the “Move” icon (
You can quickly select all blocks by selecting one and pressing Ctrl/⌘ + A, or selecting a range of blocks starting with the first and then Shift-clicking the last.
#Additional View Modes
The Cards and Cards grid view modes provide many of the same management tools, but the entries are represented as read-only cards. Double-click any card to edit its content in a slideout, or use the “Move” icon (
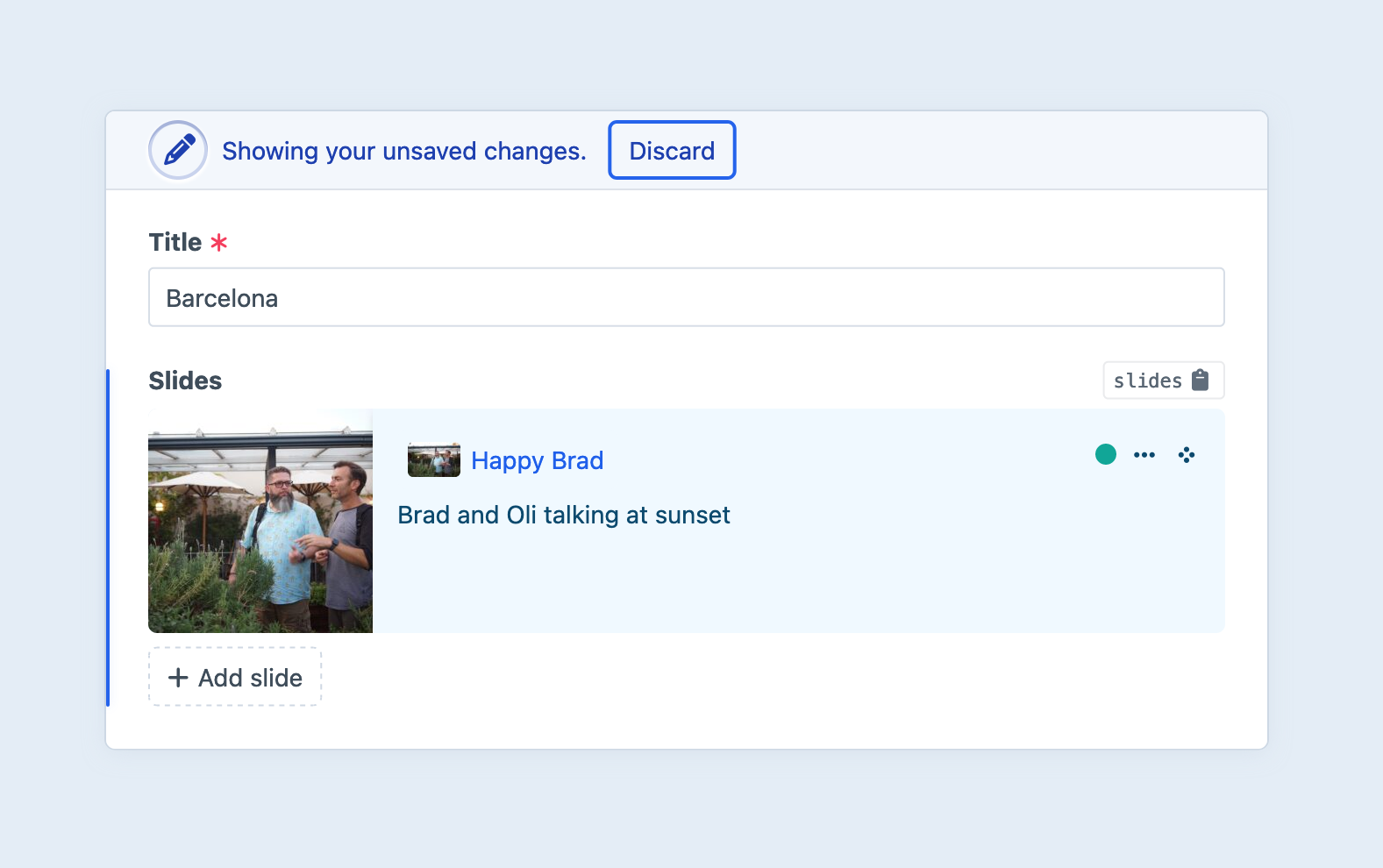
Finally, the Index view mode behaves just like a normal element index—except it only ever shows the entries owned by that field. This mode is perfect for large data sets that may span multiple pages, need to be dynamically searched or sorted by nested fields, or that would otherwise be unwieldy as blocks or cards.
#Nesting Matrix Fields
A Matrix field can include an entry type that has another Matrix field (or the same Matrix field) in its field layout. Those Matrix fields can use the same view mode, or different view modes, depending on how they’re composed. Take care when designing your authoring experience to avoid confusing or infinitely-recursive data structures.
The Cards, Cards grid, and Index view modes always open nested entries in a slideout, which can be used to break up complex content models.
#Development
#Querying Elements with Matrix Fields
When querying for elements that have a Matrix field, you can filter the results based on the Matrix field data using a query param named after your field’s handle.
Possible values include:
| Value | Fetches elements… |
|---|---|
':empty:' | that don’t have any nested entries. |
':notempty:' | that have at least one nested entry. |
{# Fetch entries whose Matrix field `myFieldHandle` has at least one nested entry: #}
{% set entries = craft.entries()
.myFieldHandle(':notempty:')
.all() %}
// Fetch entries whose Matrix field `myFieldHandle` has at least one nested entry:
$entries = \craft\elements\Entry::find()
->myFieldHandle(':notempty:')
->all();
If you have a reference to a nested entry, you can get the owner element via entry.owner.
#Working with Matrix Field Data
If you have an element with a Matrix field in your template, you can access its nested entries via the field’s handle:
{% set nestedElements = entry.myFieldHandle %}
That will give you an Entry query, ready to load all the nested entries for a given field. To fetch the nested elements, call one of the query execution methods, or use it in a loop:
{% set nestedEntries = entry.myFieldHandle.all() %}
{% if nestedEntries|length %}
<ul>
{% for nestedEntry in nestedEntries %}
{# ... #}
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endif %}
All the code you put inside the for-loop will be repeated for each nested entry. Each time, nestedEntry will be a craft\elements\Entry (opens new window) model populated with that nested entry’s content.
Here’s an example of what the template might look like for a Matrix field that has four entry types (Heading, Text, Image, and Quote). We can treat each entry type separately by checking its handle:
{% for nestedEntry in entry.myFieldHandle.all() %}
{# Grab the entry type’s handle for comparison: #}
{% set typeHandle = nestedEntry.type.handle %}
{% if typeHandle == 'heading' %}
<h3>{{ nestedEntry.heading }}</h3>
{% elseif typeHandle == 'text' %}
{{ nestedEntry.text|markdown }}
{% elseif typeHandle == 'image' %}
{% set image = nestedEntry.image.one() %}
{% if image %}
{{ image.getImg('thumb') }}
{% endif %}
{% elseif typeHandle == 'quote' %}
<blockquote>
<p>{{ nestedEntry.quote }}</p>
<cite>– {{ nestedEntry.cite }}</cite>
</blockquote>
{% else %}
{# Uh oh! This entry type isn’t support yet... #}
<p>You can output something here to remind yourself to handle additional cases!</p>
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
Craft is aware of any overridden entry types handles and labels, so comparisons against typeHandle are specific to the context.
This code can be simplified using the switch tag.
#Other Query Methods
If you only want the first nested entry, call one() (opens new window) instead of all(), and make sure it returned something:
{% set firstNestedEntry = entry.myFieldHandle.one() %}
{% if firstNestedEntry %}
{# ... #}
{% endif %}
$firstNestedEntry = $entry->myFieldHandle->one();
if ($firstNestedEntry) {
// ...
}
If you only want to know the total number of blocks, call count() (opens new window).
{% set total = entry.myFieldHandle.count() %}
<p>Total nested entries: <strong>{{ total }}</strong></p>
$total = $entry->myFieldHandle->count();
If you just need to check if there are nested entries added to a field (but don’t need to actually load them), call exists() (opens new window):
{% if entry.myFieldHandle.exists() %}
<p>Here be nested content!</p>
{% endif %}
if ($entry->myFieldHandle->exists()) {
// There’s at least one nested entry!
}
Read more about query execution methods on the element query page.
You can set parameters on the query, as well. For example, to only fetch nested entries that use a specific entry type, set the type param:
{% set nestedTextEntries = entry.myFieldHandle
.type('text')
.all() %}
$nestedTextEntries = $entry->myFieldHandle
->type('text')
->all();
#Eager Loading
Nested entries can be eager-loaded with their owners to greatly improve performance in situations when you need to output one or more nested entries within a list of other elements.
Take this list of recipes, where steps is a Matrix field:
{% set latestRecipes = craft.entries()
.section('recipes')
.orderBy('postDate DESC')
.limit(5)
.all() %}
{% for recipe in latestRecipes %}
<article>
<h2>{{ recipe.title }}</h2>
{{ recipe.summary|md }}
<div>
{{ recipe.estimatedTotalTime }}
—
{{ recipe.steps.eagerly().count() }} Step(s)
—
{{ recipe.difficulty }}
</div>
</article>
{% endfor %}
#Saving Matrix Fields
Working with nested entries is significantly more complex than other field types. The examples that follow assume some familiarity with routing and forms, as well as a willingness to adapt the provided HTML (or extend it with JavaScript) to suit your needs.
If you have an element form (such as an entry form (opens new window)) that needs to manage content within a Matrix field, that data must be sent in a specific structure. We’re using JSON for the sake of its simple syntax, but the following examples will show you how to build a similarly-structured request with normal HTML form elements:
{
"sortOrder": [
321,
654,
"new:1"
],
"entries": {
"321": {
"type": "myFirstTypeHandle",
"fields": {
"myTextFieldHandle": "...",
"myAssetField": [
4,
5,
6
]
}
},
"654": {
"type": "myOtherTypeHandle",
"fields": {
"myNumberField": 42,
"myDateField": {
"date": "2023-01-01",
"time": "00:00",
"timezone": "America/Los_Angeles"
}
}
},
"new:1": {
"type": "myFirstTypeHandle",
"fields": {
"myTextFieldHandle": "...",
"myAssetField": []
}
}
}
}
The sections beginning with highlighted lines are covered below.
#Entry Order
sortOrder should be submitted as an array of all the entry IDs you wish to persist (as well as any new entry identifiers), in the order they should be saved.
If you want all existing entries to persist in the same order they are currently in, then use this template to define your sortOrder array:
{% if entry is defined %}
{% for nestedEntryId in entry.myFieldHandle.anyStatus().ids() %}
{{ hiddenInput('fields[myFieldHandle][sortOrder][]', nestedEntryId) }}
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
The sortOrder input elements do not need to be adjacent in the DOM—you are free to distribute and collocate them with each entry’s data, if you wish. Wherever they are, though, they must ultimately be POSTed to Craft in the structure above.
#Entry Data
All of your entry data should be nested under a entries key, indexed by their ID. Each nested entry must submit its type (using the desired entry type’s handle) and custom field data nested under a fields key.
Here’s how you can output form fields for existing entries, for a Matrix field with two entry types (text and image):
{% for nestedEntry in entry.myFieldHandle.all() %}
{# Prefix the nested entry’s input names with `fields[myFieldHandle][entries][<NestedEntryId>]` #}
{% namespace "fields[myFieldHandle][entries][#{nestedEntry.id}]" %}
{{ hiddenInput('type', nestedEntry.type) }}
{% switch nestedEntry.type %}
{% case 'text' %}
{# Output fields relevant to the “Text” entry type: #}
<textarea name="fields[myTextFieldHandle]">
{{- nestedEntry.myTextFieldHandle|raw -}}
</textarea>
{% case 'image' %}
{% set images = nestedEntry.myAssetFieldHandle.all() %}
{% if images|length %}
<ul>
{% for image in nestedEntry.myAssetFieldHandle.all() %}
<li>
{{ image.getImg({ width: 100, height: 100 }) }}
{{ hiddenInput('fields[myAssetFieldHandle][]', image.id) }}
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endif %}
{% endswitch %}
{% endnamespace %}
{% endfor %}
Outputting form fields for existing nested entries is completely optional. As long as those entries’ IDs are listed in the sortOrder array, they will persist even if their content was omitted from the form data.
Craft also accepts nested entries’ UUIDs under the sortOrder key, so long as the entries are indexed with UUIDs prefixed by uid:. The structure would then look like this:
{
"sortOrder": [
"a86e9189-3bc8-4e87-ba52-58222b44c066",
"8e7f2123-e684-4075-8680-175c5e4ab215",
],
"entries": {
"uid:a86e9189-3bc8-4e87-ba52-58222b44c066": {
// ...
},
"uid:8e7f2123-e684-4075-8680-175c5e4ab215": {
// ...
},
}
}
#New Entries
To add an entry from a front-end form, you’ll need a unique, temporary identifier for it, prefixed with new:. Append that “ID” to the sortOrder array, and use it when constructing the entry’s form inputs.
For example, the first new entry that is added to the form could have an “ID” of new:1, so its type input name would end up looking like this (ignoring for a moment any namespace tags):
<input type="hidden" name="fields[myFieldHandle][new:1][type]" value="text" />
Then define the form inputs for any additional entries that should be appended to the input.
{{ hiddenInput('fields[myFieldHandle][sortOrder][]', 'new:1') }}
{# Prefix the entry’s input names with `fields[myFieldHandle][entries][new:1]` #}
{% namespace "fields[myFieldHandle][entries][new:1]" %}
{# This hidden `type` input will be expanded like the example above: #}
{{ hiddenInput('type', 'text') }}
{# Custom fields still need the `fields` prefix: #}
<textarea name="fields[myTextFieldHandle]"></textarea>
{% endnamespace %}
If you want to make the new entry optional, you will need to give the user an opportunity to remove the inputs so they are not included in the request.
The flexibility of Matrix fields often demands some client-side JavaScript—appending form fragments for different entry types, generating temporary IDs, rearranging entries and updating sort order, etc. are all difficult problems to solve with plain HTML. Craft’s UI relies on a host of control panel-specific scripts and markup—and therefore is generally not usable in the front-end.
However: as long as the data you ultimately POST to Craft conforms to the schema above, it will work! If you have a preferred view library like Vue or React, you may be better prepared than you think—your task then shifts from dealing with manipulating DOM elements to transforming your components’ state into a FormData object (opens new window) with the right parameter names and values.
#Validation Errors
Should you encounter validation issues within a Matrix field, Craft will set a flash and add errors to the main element (under the Matrix field’s handle)—as well as on each nested entry with problems.
In these cases, it’s important to handle the nested entry data appropriately—the entries will be available directly on the main element as an array, and do not need to be fetched. In fact, trying to re-load the entries from the database would mean you are working with the last-persisted state, rather than the entries populated from the most recent request!
Instead, we’ll try three values:
- Attempt to use the field value as an element query (load the entries fresh, assuming there are no pending changes hanging in-memory);
- Accept the value, verbatim (assuming Craft has left the in-memory entries attached, and they don’t need to be queried);
- Default to an empty array (this ensures whatever uses the
nestedEntriesvariable later on can safely assume it’s an array);
{% set nestedEntries = entry.myFieldHandle.all() ?? entry.myFieldHandle ?? [] %}
The null-coalescing operator (opens new window) swallows errors that occur when attempting to access variables, properties, or methods that don’t exist.
Temporary identifiers on new entries do not need to stay the same between requests (say, if you created two entries but changed their order, then submitted and hit a validation error); you may output “new” entries in the order Craft has provided them, re-keying those entries:
{% for nestedEntry in nestedEntries %}
{% set id = nestedEntry.id ?? "new:#{loop.index}" %}
{{ hiddenInput('sortOrder[]', id) }}
{{ hiddenInput("entries[#{id}][type]", nestedEntry.type.handle) }}
{# ... #}
{% endfor %}